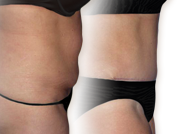
Guide to Cellulite Reduction Treatments
Cellulite is an extremely common cosmetic issue that in the past has been notoriously difficult to treat. Thanks to new non-surgical technologies, cosmetic surgeons now can more effectively address the structural causes of cellulite, helping to reduce the characteristic dimpling and restore a smoother, firmer texture to skin affected by cellulite. Choose from the links below to learn more about your options:
- What causes cellulite? Why do I have it?
- Am I a good candidate for cellulite reduction?
- What are my treatment options?
- Infographic guide to non-surgical body contouring options
- Choosing a provider
What causes cellulite?
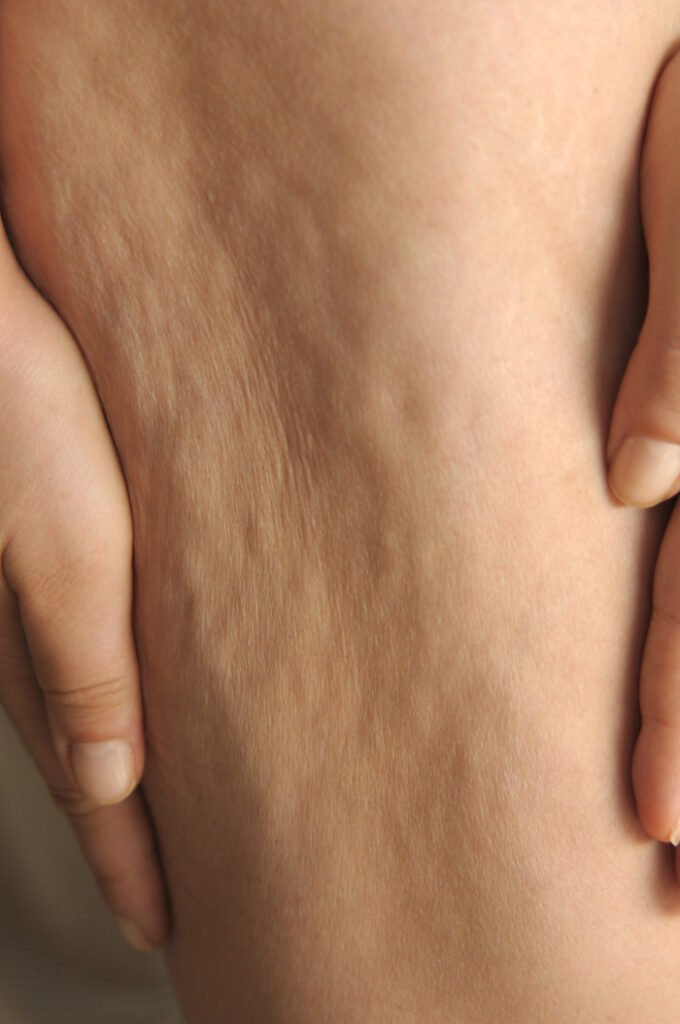
Cellulite forms when fibrous bands called septae, which connect the skin to the underlying muscle fascia, tighten irregularly, pulling down on the skin, and/or begin to break down, allowing the normal layer of fat beneath the skin to push upward. This results in the puckering or “cottage cheese” appearance.
An estimated 85 to 90% of adult women have cellulite, typically on the abdomen, buttocks and thighs. The aging process can worsen the appearance of cellulite, as skin loses elasticity and is less able to resist irregular tension created by the fibrous bands. While overweight individuals tend to have more pronounced cellulite, it is common even in very lean women, and losing weight rarely gets rid of cellulite altogether.
Am I a good candidate for cellulite reduction?
While it’s actually more common than not for women to have cellulite, the dimpled, irregular appearance is bothersome to many women. If you are unhappy with cellulite on your body, then cellulite reduction can help you feel more confident in your appearance. In general, cellulite treatment will be most effective if:
- You are bothered by the effect cellulite has on your appearance, and wish to reduce it
- You are happy with your current body weight and not significantly overweight
- You are in good overall health
- You have realistic expectations—cellulite reduction treatments can reduce dimpling, but not totally eliminate it
- Key Benefits
- Glossary
- Reduces cellulite: Cellulite reduction procedures, such as Cellfina and Velashape, can reduce the appearance of dimpled or lumpy skin caused by cellulite, particularly on the thighs and buttocks.
- Smoothes out skin: In addition to reducing cellulite, cellulite reduction procedures can also smooth out skin texture, creating a more toned appearance.
- Enhances body contour: By reducing cellulite and smoothing out skin, cellulite reduction procedures can also complement your body contour and shape.
- Cellulite: The dimpled or lumpy appearance of the skin, especially on the thighs and buttocks, caused by the underlying structure of fat deposits and connective tissue.
- Dimpling: The formation of small depressions or indentations on the skin’s surface.
- Adipose tissue: Body fat tissue, which stores energy and provides insulation and cushioning.
- Stretch marks: Scars that appear as visible streaks or lines on the skin, often caused by rapid stretching or shrinking of the skin.
- Fascia: Connective tissue that surrounds and supports muscles, organs, and other structures in the body.
- Subcutaneous fat: Fat stored beneath the skin, typically found directly above the muscles.
- Lipedema: A chronic condition characterized by an abnormal accumulation of fat cells, primarily in the legs and sometimes in the arms, leading to a disproportionate and symmetrical enlargement.
- Connective tissue: Tissue that supports and connects different structures in the body, including skin, muscles, and organs.
- Blood circulation: The movement of blood through the blood vessels, supplying oxygen and nutrients to tissues and removing waste products.
- Lymphatic drainage: The process by which lymph fluid is transported and filtered through the lymphatic system, aiding in the removal of waste materials and toxins from tissues.
- Ultrasound waves: High-frequency sound waves used in medical imaging and therapies to visualize and target tissues beneath the skin.
- Radiofrequency energy: Electromagnetic energy used in cosmetic treatments to deliver heat to the skin and underlying tissues for various therapeutic effects.
- Laser technology: The use of focused and amplified light energy for medical or cosmetic purposes, such as skin resurfacing or hair removal.
- Estrogen: A hormone primarily responsible for the development and maintenance of female secondary sexual characteristics.
- Liposuction: A surgical procedure to remove fat deposits from specific areas of the body using suction.
- Mesotherapy: A technique involving the injection of various substances, such as vitamins, enzymes, and medications, into the middle layer of the skin to treat localized fat deposits, cellulite, and other aesthetic concerns.
- Subcision: A minimally invasive procedure in which a needle is inserted under the skin to break up fibrous bands and release tethered tissue, often used to improve the appearance of cellulite.
- Acoustic wave therapy: A non-invasive treatment that uses sound waves to stimulate tissue development and promote healing, commonly used to address cellulite, improve circulation, and reduce pain.
What are my treatment options?
Cosmetic surgeons use a variety of treatments to help patients reduce cellulite. While none are permanent, many can achieve results that last a year or longer. Below, we’ve outlined the most commonly used treatment types and brand name applications—availability of these or any other treatment will vary depending on what cosmetic surgeons in your area offer.
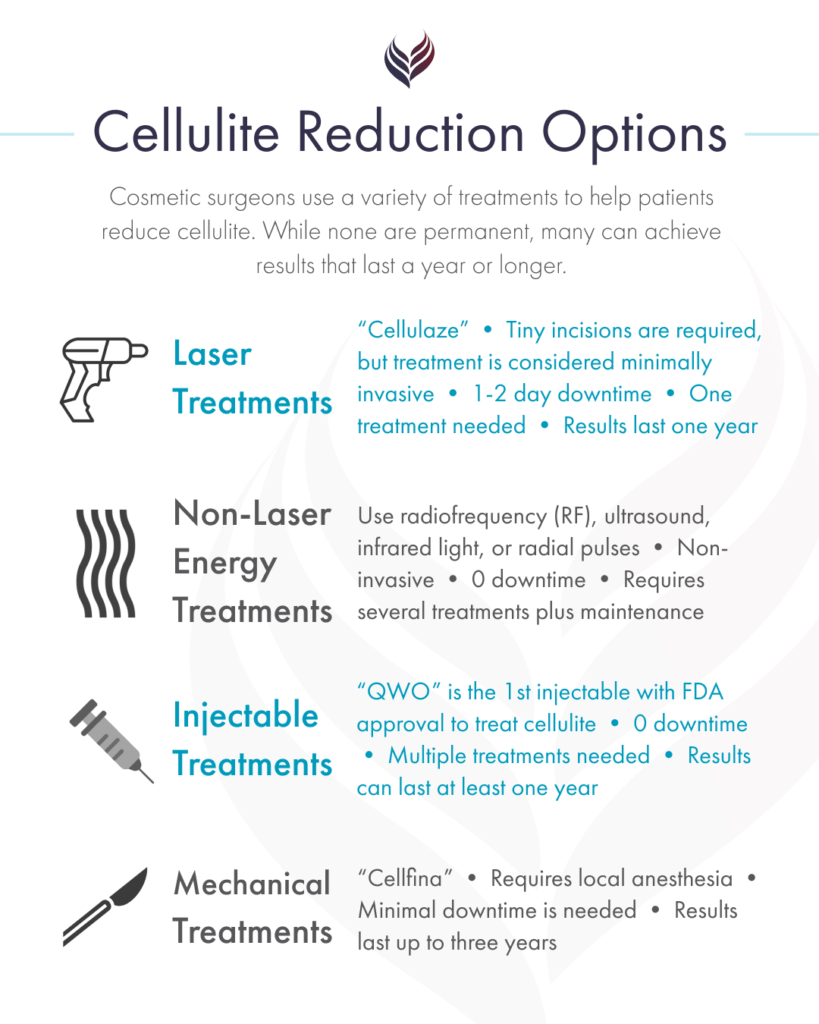
Laser treatments (Cellulaze®)
Laser cellulite reduction (the FDA cleared treatment is called Cellulaze) uses a tiny laser probe, which is inserted just beneath the skin through a small incision. This laser heats the tissues beneath the skin’s surface, where it works to:
- releases some of the fibrous septae
- reduce thickness of the subcutaneous fat layer
- stimulates collagen production
- improve skin texture and elasticity
Although it involves tiny incisions, laser cellulite reduction is considered minimally invasive and can be safely performed by a qualified provider in-office, using local anesthesia. Downtime is typically limited to 1 to 2 days. Cellulaze is indicated to last about one year, and patients typically achieve their desired result after one treatment.
Non-laser energy treatments
Many treatments use energy from radiofrequency (RF), ultrasound, infrared light, or radial pulses to heat skin, stimulate collagen production and reduce cellulite. Depending on the specific treatment, energy-based cellulite reduction may also help achieve mild fat reduction and/or relax the fibrous septae to achieve a smoother, more even skin texture. Current FDA cleared treatments include:
- VelaShape® (RF and infrared light)
- Venus Freeze® (RF and pulsed electro-magnetic fields)
- ThermiSmooth® Body (RF)
- Zimmer Z Wave (radial pulse therapy)
Energy-based cellulite treatments are delivered through the skin, so they are considered non-invasive and usually require no downtime. However, a series of treatments may be recommended for optimal results. Additionally, results are temporary, so you will need to repeat treatment every few months to maintain results.
Injectable treatments (QWO®)
QWO is the first injectable with FDA approval to treat cellulite. However, as of December 2022, QWO will no longer be produced or sold by the manufacturer Endo due to excessive and unpredictable bruising side effects and the risk of prolonged skin discoloration. Still, it remains an FDA-approved product, and your cosmetic surgeon may offer any unexpired product to you with appropriate counseling about the risks of treatment.
QWO contains enzymes that break down the collagen bands that cause dimpling, reducing the appearance of cellulite without surgery. QWO is also thought to work by stimulating the production of more flexible septae and redistributing fat cells below the skin. Clinical trials showed that QWO is safe and effective when used in the buttocks of women, specifically.
The number of QWO treatments you may need varies by treatment area and size. Results were achieved in clinical trials with 3 treatments, each spaced 3 weeks apart.
Mechanical treatments (Cellfina®)
Cellfina is an FDA cleared automated mechanical cellulite reduction treatment. It works by releasing tightened septae using a very thin blade, which is inserted through a tiny incision. The skin is gently suctioned up into the Cellfina device, which allows the cosmetic surgeon to insert the blade only a few millimeters beneath the skin, minimizing impact on surrounding tissues. Local anesthesia is used.
To date, Cellfina is indicated as the longest-lasting cellulite treatment, with results lasting up to 3 years. Minimal downtime is needed, and results are noticeable within a few days after treatment. Side effects include temporary soreness and mild bruising, with serious side effects very rare when treatment is performed by a qualified physician.
Massage and topical cellulite treatments
Specialized massage techniques have been used for years as a way to address cellulite. These typically use vacuum suction or a roller to “knead” the skin and subcutaneous fat. While some patients report positive effects, improvements are temporary and any smoothing effect likely results from mild inflammation in the treatment area.
Most patients who are bothered by cellulite have tried cream or lotion that promises to improve cellulite. While certain medical grade products can help gradually improve collagen production for firmer skin, even high-quality products are rarely effective on cellulite, which requires more extensive remodeling of fat, connective tissue and collagen than a cream can provide. Cellulite creams are rarely a worthwhile investment.
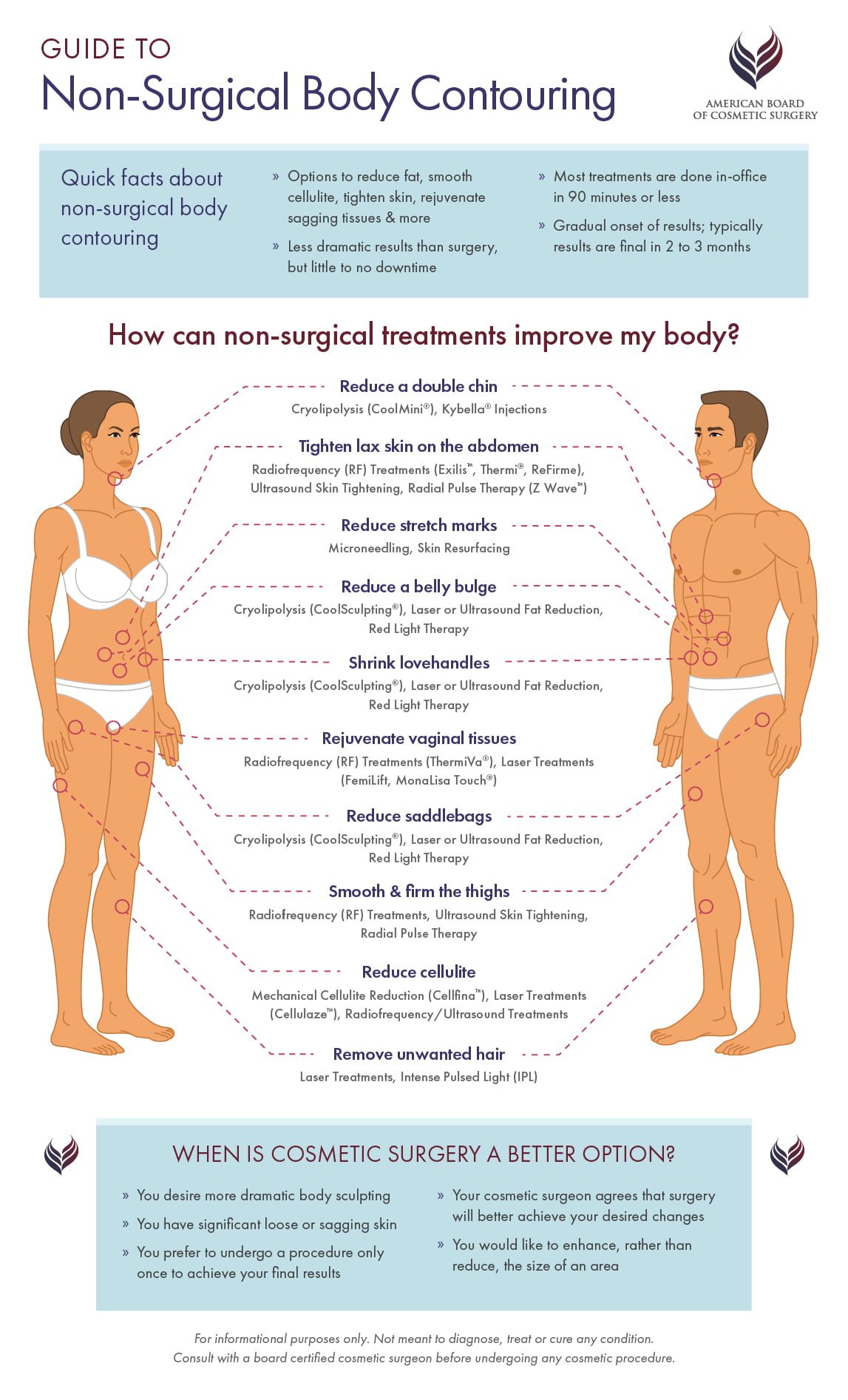
Your Non-Surgical Body Contouring Options: an Infographic Guide
Non-surgical body contouring includes much more than cellulite reduction. Today, you have options to reduce fat, rejuvenate vaginal tissues, tighten skin, and remove unwanted hair. The guide below outlines your options.
Choosing a provider for cellulite reduction
In general, non-invasive cellulite reduction (such as QWO, VelaShape, Z Wave, or Venus Freeze) can be safely performed by a licensed, trained aesthetician working under physician supervision. Treatments that require a laser, incision, or both (such as Cellulaze or Cellfina) require advanced medical training and knowledge of anatomy and should be performed only by a qualified cosmetic surgeon or provider with equivalent training and experience.

FIND AN ABCS COSMETIC SURGEON NEAR YOU »
The best place to start? Find an ABCS diplomate cosmetic surgeon near you, and schedule a consultation to discuss your needs and goals, review your treatment options, and learn whether cellulite reduction treatment is right for you.
References »
Bass, Lawrence S. MD, Kaminer, Michael S. MD. Insights Into the Pathophysiology of Cellulite: A Review. Dermatologic Surgery. 2020; doi: 10.1097/DSS.0000000000002388
Sadick N. Treatment for cellulite. International Journal of Women’s Dermatology. 2018. doi: 10.1016/j.ijwd.2018.09.002
Luebberding S, Krueger N, Sadick NS. Cellulite: an evidence-based review. American Journal Clinical Dermatology. 2015. doi: 10.1007/s40257-015-0129-5
Mirrashed F, Sharp JC, Krause V, Morgan J, Tomanek B. Pilot study of dermal and subcutaneous fat structures by MRI in individuals who differ in gender, BMI, and cellulite grading. Skin Research and Technology. 2004. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0846.2004.00072.